 |
| Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma (cSCC) |
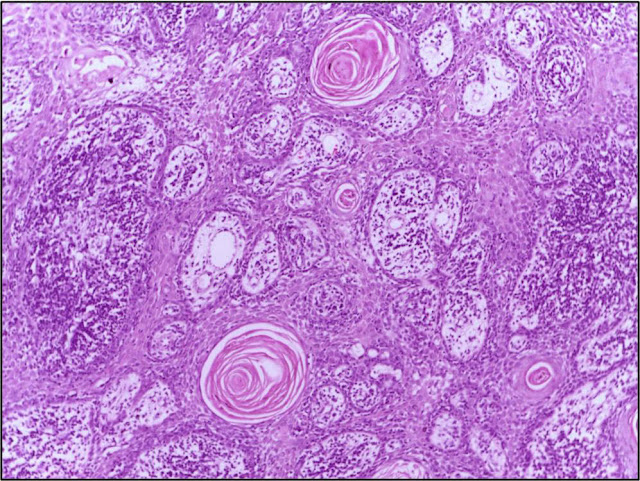
Cutaneous Squamous Cell
Carcinoma (cSCC) is the second most common form of skin cancer, with increasing
incidence rates globally. While surgical excision remains the primary treatment
modality for localized cSCC lesions, advanced or metastatic cases often require
multimodal therapeutic approaches to achieve optimal outcomes.
- Understanding Cutaneous Squamous
Cell Carcinoma: Cutaneous
Squamous Cell Carcinoma (cSCC) arises from the malignant
transformation of squamous cells in the epidermis or its appendages. It
typically presents as a firm, red nodule or ulcerated lesion on
sun-exposed skin and has the potential to metastasize to regional lymph
nodes and distant organs.
- Rationale for Combination Therapies:
Combination therapies in cSCC treatment involve the simultaneous or
sequential administration of multiple treatment modalities to target
different aspects of the disease. This approach aims to maximize
therapeutic efficacy, overcome resistance mechanisms, and minimize the
risk of disease recurrence or progression.
- Surgery and Adjuvant Therapies:
Surgical excision is the cornerstone of localized cSCC treatment, but
adjuvant therapies such as radiation therapy or topical chemotherapy may
be employed to reduce the risk of local recurrence or metastasis.
Combination approaches combining surgery with adjuvant therapies have
shown improved outcomes in high-risk cSCC cases.
- Immunotherapy and Targeted Therapy:
Immunotherapy agents, such as immune checkpoint inhibitors, have
revolutionized the treatment landscape for advanced cSCC by harnessing the
body's immune system to target cancer cells. Similarly, targeted therapy
drugs that inhibit specific molecular pathways implicated in cSCC
pathogenesis offer promising therapeutic options.
- Chemotherapy and Radiation Therapy:
Traditional chemotherapy agents and radiation therapy remain important
treatment modalities for advanced or metastatic cSCC cases. When used in
combination with surgery or other systemic therapies, they can enhance
local tumor control and improve patient survival rates.
- Emerging Therapeutic Approaches:
Ongoing research efforts are focused on identifying novel therapeutic targets
and developing innovative treatment strategies for cSCC. Combination
regimens incorporating novel agents, such as targeted kinase inhibitors or
epigenetic modulators, hold promise for improving treatment outcomes and
overcoming treatment resistance.
- Patient-Centered Care and Shared
Decision-Making: In the era of personalized
medicine, the selection of treatment modalities for cSCC should be
tailored to individual patient characteristics, tumor biology, and
treatment goals. Shared decision-making between patients and healthcare
providers is essential to ensure that treatment plans align with patient
preferences and values.
- Challenges and Future Directions:
Despite the promise of combination therapies in cSCC treatment, several
challenges remain, including treatment-related toxicities, drug
resistance, and access to novel therapies. Future research efforts should
focus on optimizing treatment regimens, identifying predictive biomarkers,
and improving patient outcomes through multidisciplinary collaboration.
Combination therapies
in Cutaneous Squamous Cell Carcinoma treatment represent a promising approach
to enhance therapeutic efficacy and improve patient outcomes. By integrating
surgical, systemic, and novel therapeutic modalities, healthcare providers can
deliver personalized and comprehensive care to patients with cSCC, ultimately
leading to better treatment outcomes and quality of life.
Tags
biotechnology
